Comparing MCP (Model Context Protocol) Gateways
The rise of Model Context Protocol (MCP) has given AI agents and large language models (LLMs) a standardized way to talk to external tools, APIs, and data sources. In theory, it solves the messy integrations and custom connectors that have slowed down real-world agent adoption. A clean protocol should mean smooth interoperability.
However, we’re observing certain patterns of fragmentation. Each MCP server runs in isolation. Agents have to handle multiple connections. And enterprises possess little control over discovery, governance, or observability. Security-wise, too, no central place exists to enforce policies or audit usage. It’s as if the ecosystem is facing risks of repeating the same clutter we saw before API gateways emerged.
An MCP gateway, acting as a unified endpoint, can route, secure, and help monitor MCP traffic. It can potentially bring the same discipline to AI agents that API gateways have brought to microservices. Several open-source and enterprise-ready gateways are already competing to define the standard of what an MCP gateway should be.
In this article, we will look at some of the MCP gateways available today and their features. We will also discuss the necessity of a dedicated analytics layer that works in tandem with the gateway to help enterprises realize their AI roadmap.
 Monitor MCP Traffic and Agent Behavior with Moesif
14 day free trial. No credit card required.
Try for Free
Monitor MCP Traffic and Agent Behavior with Moesif
14 day free trial. No credit card required.
Try for Free

What is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) Gateway?
An MCP gateway is a piece of infrastructure that functions as a centralized control plane to securely, reliably, and idiomatically connect AI agents to the growing ecosystem of MCP servers. It provides a single endpoint that simplifies discovery, security, and traffic management for MCP workloads. Thanks to MCP gateway, an agent doesn’t need to open a connection to every tool it requires. Instead, the gateway aggregates secure and trusted servers under one addressable entry point, to which the agent connects to.
We can look comparatively at traditional API gateways and MCP gateways in five dimensions:
| Dimension | Traditional API gateway | MCP gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Primary consumer | Human-driven apps and backend services | AI agents, AI assistants, large language models |
| Routing logic | Path, headers, and standard request metadata | Semantic intent, agent context, and task structure |
| Protocol | HTTP, REST; sometimes gRPC | Native support for MCP (JSON-RPC) for standardized agent-to-tool interactions |
| State management | Largely stateless, with each requests handled independently | Can preserve context across multi-step workflows; may also cache tool outputs for reusability |
| Orchestration role | Minimal; each request is isolated | Can orchestrate tool selection, chaining, or combining results across overlapping capabilities |
Why Do You Need an MCP Gateway?
An MCP gateway brings compelling benefits and solves problems that are frustrating standardized AI adoption through the Model Context Protocol.
Centralized Access and Policy Management
Enterprises are adopting more MCP servers to power their agent workflows. Without a gateway, each AI agent must manage multiple direct connections, which quickly becomes unsustainable. It results in fragmented security, duplicated integrations, and makes visibility into usage harder.
A centralized gateway can solve these issues by acting as a single access point. You avoid the hassle of implementing authentication, authorization, and rate limiting in every tool. Instead, you enforce these policies at the gateway. It also becomes a lot easier to onboard new servers and meet compliance across sensitive environments like finance or healthcare.
Foundation for Observability and Monitoring
MCP gateways also standardize traffic paths between agents and tools, the indirect benefit of which is a consistent stream of telemetry. Every call, whether successful, failed, or retried, passes through a single checkpoint. As a result, you get reliable records of usage patterns, performance, and cost drivers. Gateways themselves don’t offer advanced analytics, but they can provide the raw data and make integration with platforms like Moesif simpler and more powerful; you can achieve deeper monitoring, reporting, and business intelligence.
Scalability and Reliability
Usage in agentic AI systems can spike unpredictably. To complete a task, an agent might generate hundreds of tool calls. A gateway can handle these demands through different strategies like load balancing, cache, and request queuing. This prevents upstream MCP servers from becoming bottlenecks. It also allows enterprises to scale their agent usage without rewriting integrations or overprovisioning individual servers.
Composability and Innovation
Perhaps the most strategic role MCP gateways play is enabling composability. Since they abstract away direct connections, enterprises can mix and match different MCP servers into a single unified interface. They can be internal APIs, vendor tools, or open-source utilities; as long as they are compatible with the MCP gateway, the integration simply just works.
This reduces friction between developers and allows AI agents to perform complex, multi-step workflows that don’t possess brittle point-to-point integrations. Naturally, it also pushes innovation forward and keeps operations governable.
The Top MCP Gateways in 2025
Although still early, we already have several enterprise-ready solutions available in the market, as well as experimental open-source projects. Let’s look at some of them and their features.
WSO2
WSO2 allows you to create, discover, and manage MCP servers with a centralized control plane through the open-source API Manager (APIM) and the SaaS API management platform Bijira. This means having a unified platform where you can streamline workflows across both traditional API and agent-based AI services. You can create an MCP server from its OpenAPI spec, from an existing API, and also set up a proxy for an existing MCP server.
Conveniently, using the AI Gateway, you can create, deploy, and manage AI APIs which you can then convert to MCP servers. This way, WSO2 APIM and Bijira can build and maintain your organization’s AI capabilities end-to-end across varying business requirements and product models, all under one platform.
Docker MCP Gateway
Docker’s MCP gateway is positioned as an OSS, production-grade gateway for orchestrating and managing MCP servers from the Docker MCP catalog. It’s an obvious choice for organizations already invested in Docker and containerized apps and now wants to integrate MCP into their infrastructure. It centralizes routing, policy enforcement, and other managerial tasks. Deployment is also simple with familiar Docker Compose, both locally and in production.
Solo.io Agent Gateway
Solo.io’s Agent Gateway is another open-source project that supports MCP. It functions as a production-ready data plane for agentic AI, supporting both agent-to-agent and agent-to-tool communication. You can have multiple backend types to which Agent Gateway proxies traffic to, all under one endpoint; these types include MCP servers and other agents. Irrespective of the number or type of backends, Agent Gateway exposes only one endpoint for receiving requests. As a data plane, it helps enterprises consolidate AI tool access through a managed endpoint.
Kong AI Gateway
Kong has extended its AI Gateway to support MCP servers, allowing organizations to govern their AI tool usage through the same platform they use for API traffic. You can expose any MCP server through AI Gateway and then use plugins to establish policy enforcement, observability, and access control. It’s an appealing option for enterprises aiming to standardize traffic management across both APIs and agent workflows under one platform.
Tyk AI Studio
Tyk’s AI Studio lets you expose internal tools and APIs to AI agents. You can also convert your APIs to MCP servers with access control mechanisms in place to prevent misuse. The integrated AI Gateway provides a single entry point with built-in governance, monitoring, and security features for your AI services and deployed MCP servers. Like Kong, Tyk helps organizations manage authentication, traffic policies, and analytics consistently across both AI and API environments.
IBM ContextForge MCP Gateway
IBM’s ContextForge MCP Gateway is an open-source community project still in early beta, but not a supported IBM product. It implements a rich set of features you’d expect from an MCP gateway and also acts as an MCP registry. It can convert REST endpoints into MCP servers as well, bearing one of its goals of federating MCP and REST services. While not enterprise-backed, it adds diversity to the ecosystem and provides a way for experimentation, especially for multi-agent and multi-tool orchestration.
Microsoft’s MCP Gateway Solutions
Microsoft supports MCP gateway capabilities in two ways:
- The open-source MCP gateway provides traffic routing and control plane for MCP servers in Kubernetes environments, including enterprise-ready integrations for security and observability.
- Azure API management acts as an auth and security gateway for MCP servers, leveraging Azure APIM’s scalability as integrations grow.
Lunar MCPX
Lunar.dev MCPX offers a comprehensive orchestration and security solution for MCP servers and tools. Its focus areas include centralized tool usage, granular and configurable access control, authorization, and Prometheus-compatible metrics. MCPX is one of the first purpose-built MCP gateways, designed to help enterprises with their growing catalogs of MCP servers and AI agent workflows. They have an open-source solution as well, and pricing plans for both free and commercial usage.
The following table summarizes the different aspects of the gateways we’ve discussed so far.
| Gateway | Offering type | Primary focus | Ideal use cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| WSO2 | Open-source and enterprise | Open-source and SaaS control plane for complete lifecycle management of MCP servers using one platform | Feature-rich open-source solution for prototyping and evaluating use cases, or SaaS solution for enterprise-grade MCP use cases |
| Docker MCP Gateway | Open-source and enterprise-ready | Unified MCP endpoint for MCP servers in Docker MCP Catalog, container-native integration | Enterprises already using Docker and have containerized workloads |
| Solo.io Agent Gateway | Open-source | Data plane for agent-to-agent and agent-to-tool communication in agentic AI systems | Enterprises consolidating AI usage through a managed endpoint |
| Tyk AI Studio | Commercial | Unifying and controlling AI usage, improving developer and customer experience | Exposing internal APIs and tools to AI agents in enterprise use cases |
| IBM ContextForge | Open-source | Unified access point for AI usage and federation of REST and AI services | Developers and researchers evaluating AI usage in hybrid backend architectures consisting of RESTful and MCP-based services |
| Microsoft | Open-source and commercial | Open-source gateway solution for MCP servers in Kubernetes environments Enterprise-grade auth gateway for MCP servers , supporting security and scale | Developers prototyping MCP, or enterprises using Azure API Management. |
| Lunar MCPX | Free and commercial | Orchestration, security, and management for enterprise MCP usage | Large organizations building complex agentic AI systems |
The Importance of Analytics for MCP Gateways and Agentic AI
MCP gateways solve the operational challenge of consolidating the management of MCP-compatible tools, their usage, and lifecycles. However, to build reliable and cost-effective AI systems, you need a dedicated platform like Moesif that allows you to observe past basic telemetry and logs.
Understanding Agent Behavior at Scale
AI applications and agents are not predictable clients. They may call multiple tools in succession, retry failed calls, or generate traffic bursts unlike anything we see in human-driven apps. If there’s a surge in requests, it could be either productive automation or an agent stuck in a loop. Traditional gateway metrics won’t reveal the difference. But analytics capable of correlating agent identity, tools, and session context can.
Linking MCP Server Usage to Costs and Outcomes
Each MCP request carries costs, whether that’s compute cycles, API credits, or licensing fees. Gateways aren’t designed to explain who is driving those costs or whether those calls lead to successful outcomes that define the actual value enterprises get from your product. To make roadmap and pricing decisions, product and finance teams need metrics like cost per successful tasks and adoption by customer segment. Without this attribution layer, MCP adoption risks cost overruns with little accountability.
Making Continuous Optimization
Analytics also promotes iteration. It makes engineering leaders knowledgeable about:
- Underperforming services
- Workflows incurring failures the most
- Adoption of new MCP servers or tools
Analytics platforms provide customizable performance analytics that you can associate with various parameters, like specific servers, agents, or tools. These provide valuable insights to act on and improve agent workflows and prioritize engineering investments.
Monitoring in Real Time
Without real-time monitoring, it’s impossible to stay on top of the high risks that come with the dynamic and unpredictable nature of AI agents. Real-time analytics tools not only detect anomalies according to your specification, but also provide configurable means to dispatch alerts in real time to appropriate channels. This allows you to resolve issues before they escalate and improve user experiences.
Moesif’s Role in MCP Gateway for Analytics and Observability
Moesif adds actionable analytics and observability as your MCP system scales through the gateway to more and more agent workflows. It provides the longitudinal analytics necessary for better and confident decision making without stressing or altering your gateway’s role; for example:
- Churning agents
- Tools driving the most outcomes
- Behavioral changes
- Anomalies
Insights like these allow engineering and product teams to run AI systems reliably, cost-effectively, and with confidence. And Moesif unifies all of this even if your setup involves multiple MCP servers or gateways, with native integrations available for platforms like WSO2, Kong, and Tyk.
Deep Visibility into Agent and Tool Behavior
You can use Moesif to enrich your MCP traffic with agent identity, session context, and tool-level metadata; for example, consider fields like these:
agent_idmcp_serverretry_count
Moesif can capture the entire request and response context, including headers. So you can add custom headers as well, for example, to tie usage back to specific customers and teams, or attach token consumption information.
For example, here’s some MCP traffic data in Moesif’s real-time Live Event Log:
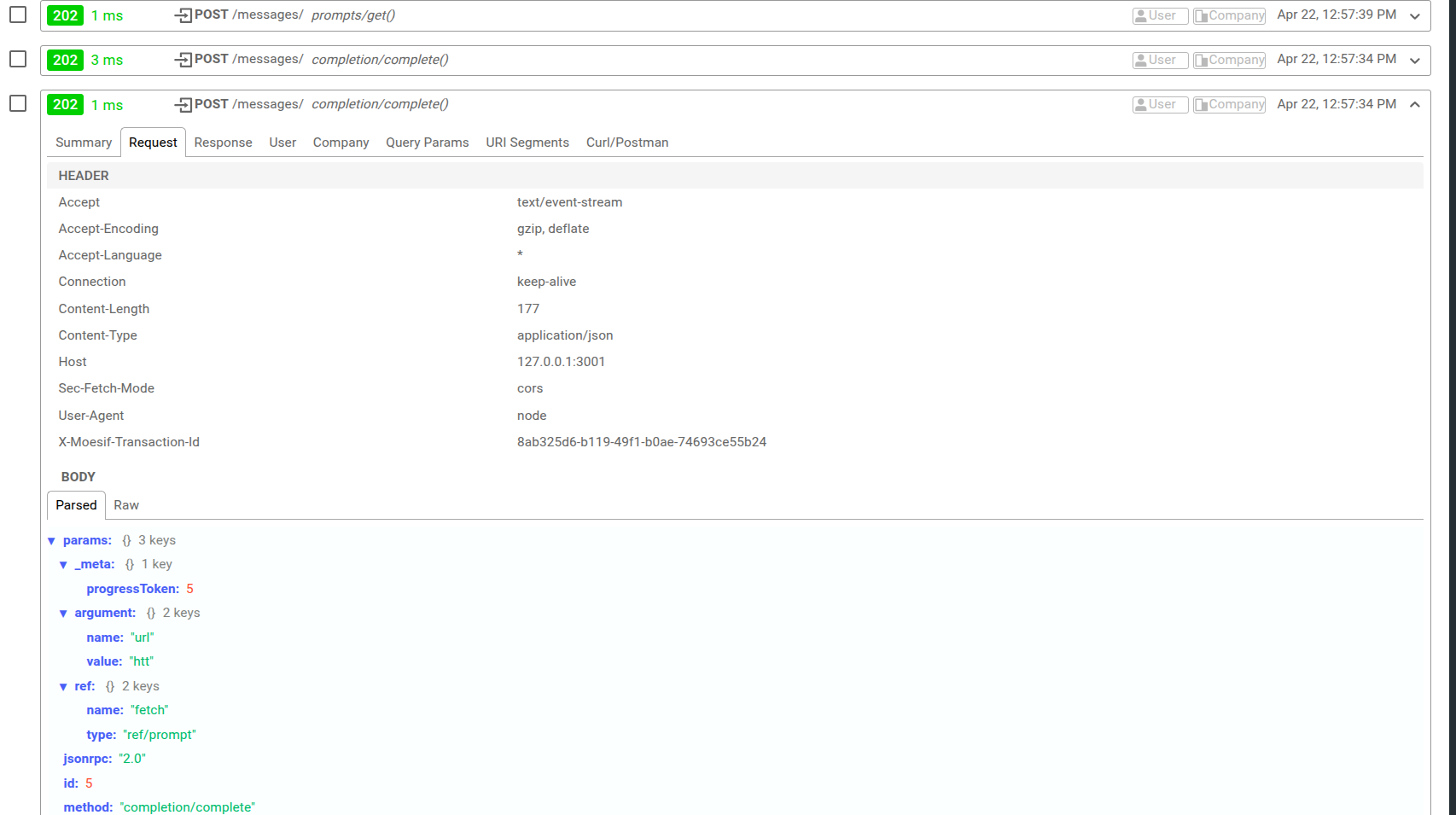
Moesif also supports tracking custom actions outside typical HTTP activities. For example, in streaming or SSE (Server-Sent Events), you can emit a “start” and a “complete” event to get an end-to-end visibility into a workflow through Moesif. Moesif’s OpenTelemetry support also allows you to capture span actions.
See the article Monitoring MCP Security and Agent Behavior with Moesif for a more detailed discussion about making agent and tool behavior observable.
Business-Level Cost Attribution
Moesif maps the requests flowing through your gateway to customers, teams, and agents. This opens up different ways to analyze usage and surface metrics like cost for each completed task or customer segment. It becomes easier to understand things like adoption patterns and true ROI of adding or deprecating tools. Using such insights, you can align engineering capacity with business values. Apart from tracking costs, Moesif can also help you monetize your MCP servers.
KPIs Dashboards with Custom Analytics
Engineering leaders can create real-time analytics dashboards, for example, to track percentile latencies like P90 and failure rates per tool and per MCP server. For example, here we look at average latency by JSON-RPC method using a time series:
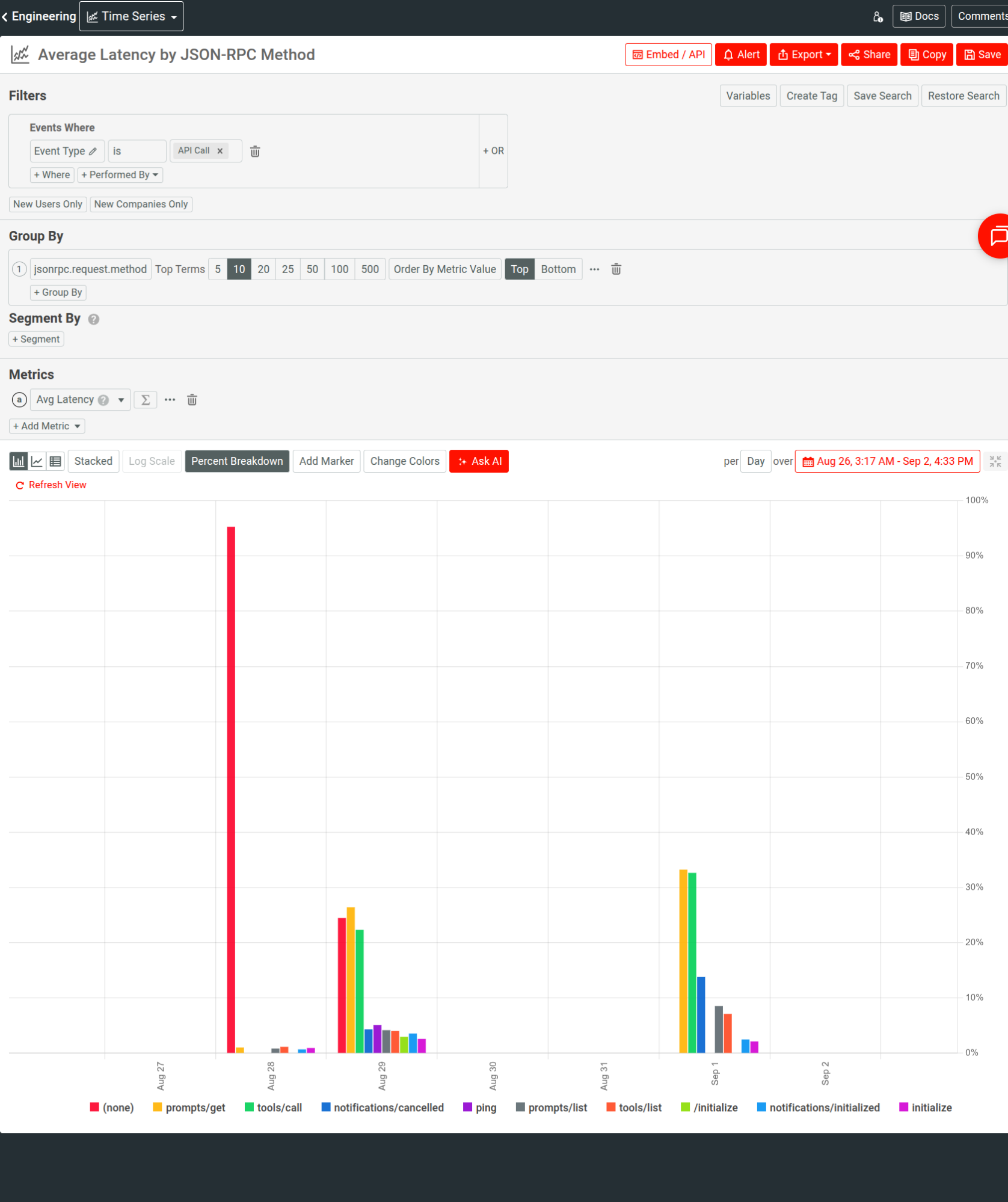
Having agent and server data as first-class analytics entities means you can easily correlate error spikes with specific tools or versions and highlight regressions by different criteria.
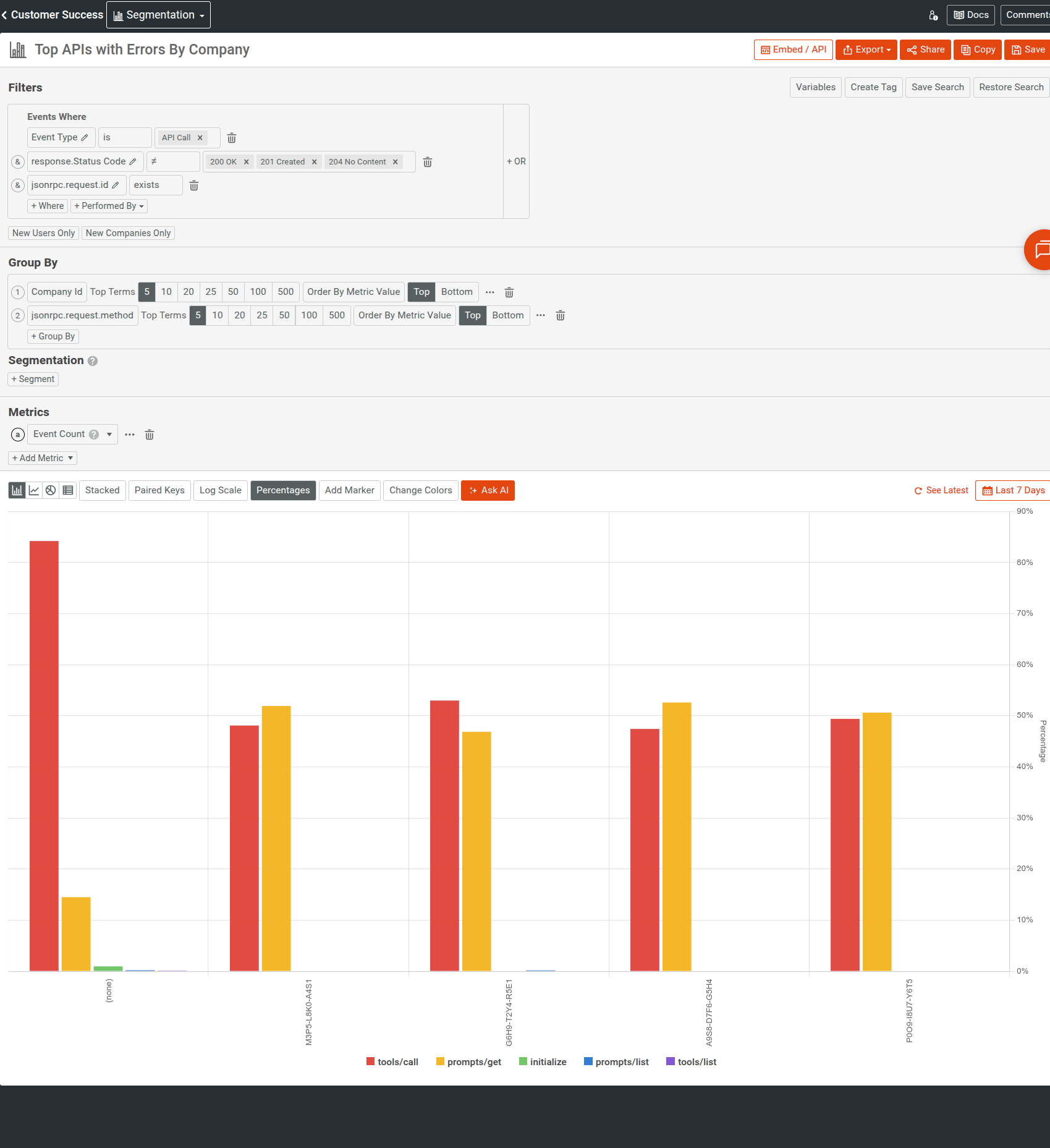
Product and platform teams can monitor activation funnels, task success and error rate, and cost per successful task by agent, tool, and customer segment. For example, the following Segmentation analysis looks at API errors in an MCP server, broken down by company ID and JSON-RPC method:
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
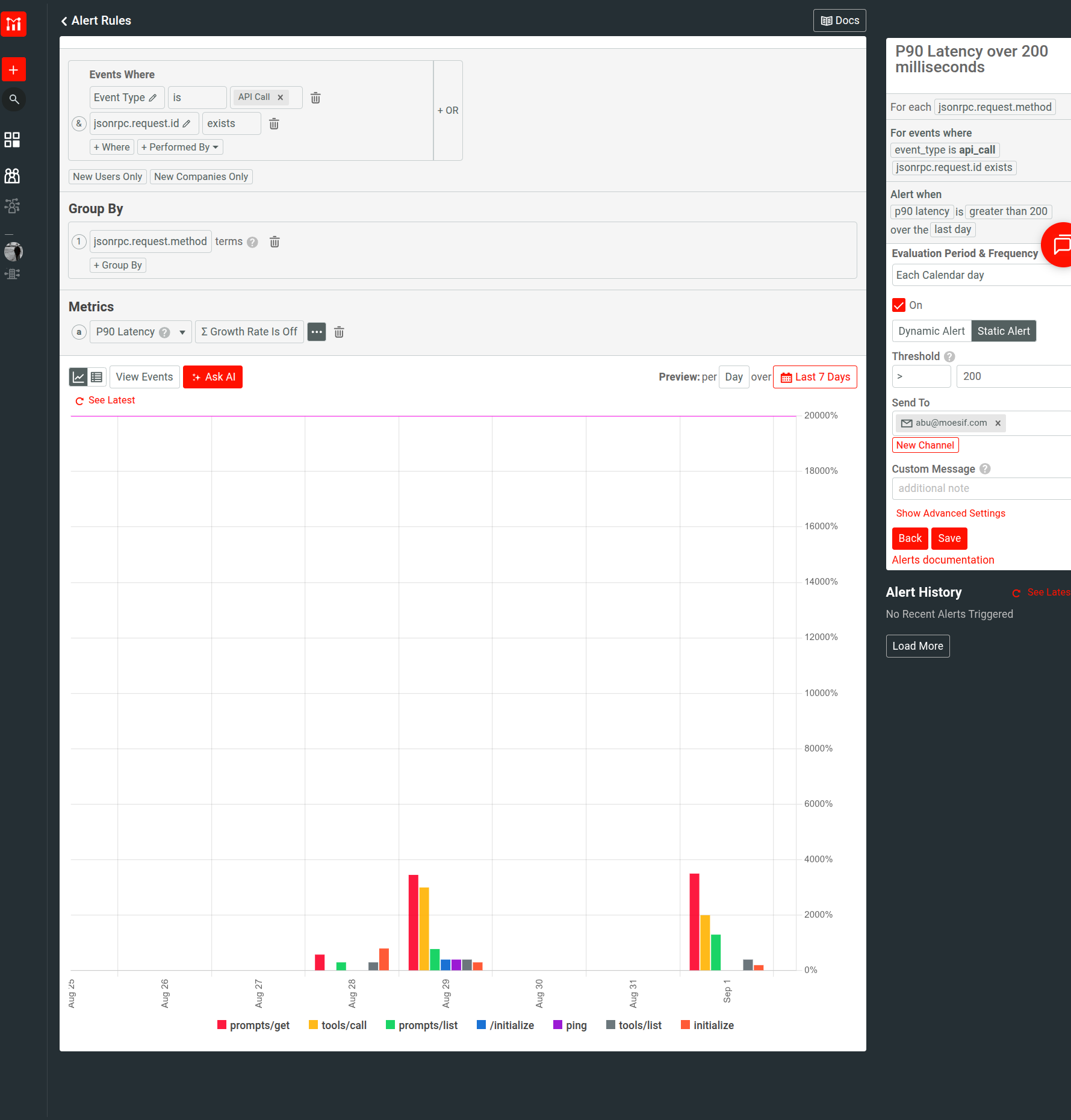
Moesif’s robust monitoring features can detect anomalies in real-time and route alerts to the right teams. You can customize every step of what you want to monitor, alert criteria and type, and where you want Moesif to dispatch those alerts. For example, you can set up alerts for agents crossing quota limits, or a specific server experiencing degraded performance.
For example, here we set up an alert to monitor latency: Moesif alerts you whenever the threshold P90 latency of 200 milliseconds is exceeded:
Conclusion
MCP gateways are quickly becoming a major component in how enterprises scale their AI infrastructure and succeed. As agentic AI systems get more adoption through the MCP standard, we also need systems that don’t collapse under erratic agent behavior. Enterprises also need to make sure their efforts drive measurable value rather than hidden costs.
Without a gateway, every new tool integration becomes an operational burden, since there’s nothing to centralize traffic and governance. And without proper analytics, it’s impossible to grow since there’s no data to base decisions on. That’s where Moesif comes in, supporting business goals by layering on analytics and observability that can tackle the unpredictable nature of AI systems. This way, enterprises possess both the control to govern their AI systems and the intelligence to improve it over time.





